Honeybee is the common name for any of several species of highly
social bees known for their honey-hoarding behaviour and their use as a
domesticated species.
The European honeybee is important in modern agriculture
and in nature, providing pollination for many valuable crops and wild plants.
It is native to Asia and the Middle East and was introduced to North America by
early European colonists. By the mid-1800s honeybees had become widespread.
Today, they are naturalized on every continent except Antarctica. Honeybees can
be easily reared, are adaptable to many climates and to laboratory conditions,
and have a complex life cycle. They are among the most studied and best known
insects.
Diversity
In addition to the familiar European
honeybee, there are six other recognized species of honeybees, including the
Indian honeybee, Koschevnikov's honeybee, the dwarf honeybee, the andreniform
dwarf honeybee, the giant honeybee, and the mountain giant honeybee.
The European, the Indian, and to some extent the dwarf honey bees are the species
that have been domesticated, although the European honey bee is by far the most
widespread domesticated bee and the only species kept in North America.
There are many races of the European honeybee. The ones most popular in modern
beekeeping are the Italian, Carniolan, and Caucasian. Most honeybees used in
hives today are mixtures of these and sometimes other races. Africanized
honeybees, also known as killer bees, are a hybrid of African and European
races naturalized in the western hemisphere.
Social Organization
The honeybee is a social insect that can
survive only as a member of a colony. The colony inhabits an enclosed cavity,
its nest. Domesticated colonies are kept in artificial containers, usually
wooden boxes, known as hives.
Their social organisation is extremely complex, and consists of several castes.

Castes
The honeybee community consists of three structurally different forms-the
queen (reproductive female), the drone (male), and the worker (nonreproductive
female). These castes are associated with different functions in the colony;
each caste possesses its own special instincts geared to the needs of the
colony.
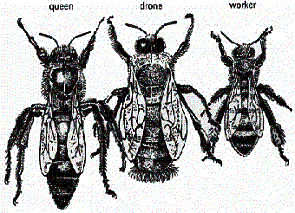
A comparison of different bees and their respective sizes
A Queen Bee and a Worker, to scale